Robotic Process Automation (RPA) was the first big stride toward automation, eliminating repetitive, rule-based, and mundane tasks, driving operational efficiency.
However, as workflow becomes more complex and data-heavy, one question arises: “How can enterprises scale automation beyond simple tasks with RPA?” Because it lags behind evolving needs, especially in heavily regulated industries such as customer support.
In fact, only 3% of enterprises have scaled RPA across the organization, citing challenges in flexibility and integration. (Source: Deloitte)
That’s where intelligent process automation steps in, handling more complex tasks with greater efficiency and uncovering new possibilities for innovation and business growth.
This blog explains what robotic process automation and intelligent process automation are and how they differ from each other. And as automation continues to evolve, we’ll also explore the next frontier, agentic automation.
Table of Contents
- What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
- What is Intelligent Process Automation?
- Why Enterprises Are Replacing RPA with Intelligent Automation
- From Intelligent to Agentic Automation: The Next Frontier
- Leverage Next-Gen Automation with SearchUnify Agentic AI Suite
- FAQs
What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
RPA is an automation technology that automates business processes. It utilizes software bots, automating repetitive and rule-based tasks such as automated responses to customers, invoice processing, data entry, and many more.
RPA executes tasks like a human, but with speed and accuracy. It is deterministic, following predefined rules and logic, and structured data inputs. However, it struggles when input changes, complexity arises, or it needs to process unstructured formats. Additionally, it cannot adapt, learn, or make any judgment call, even requiring additional help to expand workflow capabilities.
As a result, RPA often falls short in execution. Nearly two-thirds (63%) of organizations said implementation took longer than expected, and over a third (37%) found costs exceeded their estimates, revealing the cracks in traditional automation. (Source: Deloitte)
Now, enterprises are re-evaluating their decision to leverage RPA and exploring more intelligent automation options.
What is Intelligent Process Automation?
Intelligent process automation is sometimes called intelligent automation or cognitive automation. It combines automation technologies such as RPA or business process management (BPM) with AI technologies, such as NLP, ML, computer vision, predictive analytics, and cognitive computing. This combination enables business process automation that can think, learn, and continuously optimize itself without constant human input.
Intelligent automation streamlines business operations by letting it manage repetitive to complex tasks. For example, a support organization might use intelligent automation to automate customer interaction and quickly resolve their queries without human intervention. It not only frees up resources but also improves operational efficiencies, reducing potential for human error.
Why Enterprises Are Replacing RPA with Intelligent Automation
Limited to Structured Data
As we mentioned above, RPA can process structured data, yet in the context of unstructured data such as images, audio files, emails, and articles, it fails to process. The reason? RPA follows the pre-set script and cannot comprehend the context, meaning, or sentiment within the unstructured data. Additionally, it can’t handle variation in document layouts; even a single change in customer query input can break automation.
Suppose an organization uses a rule-based chatbot (RPA) for enhancing self-service. However, it can only respond to queries it’s been explicitly programmed for.

How Intelligent Automation Overcomes This
Intelligent automation leverages NLP, computer vision, and machine learning. With NLP, it understands the context and intent in text-based documents or queries, and with computer Vision, it can read images, scanned documents, or screenshots to extract relevant information like order IDs, error codes, or product labels.
Additionally, ML analyzes large volumes of past unstructured data to identify recurring issues and suggest the best actions or responses. It connects with CRMs, ticketing systems, and knowledge bases to cross-reference and validate unstructured inputs, ensuring context-aware responses.
This empowers support teams to deliver smarter, context-rich assistance while significantly improving customer satisfaction and efficiency.
Imagine an organization uses Intelligent automation for enhancing self-service. Here’s how it works.
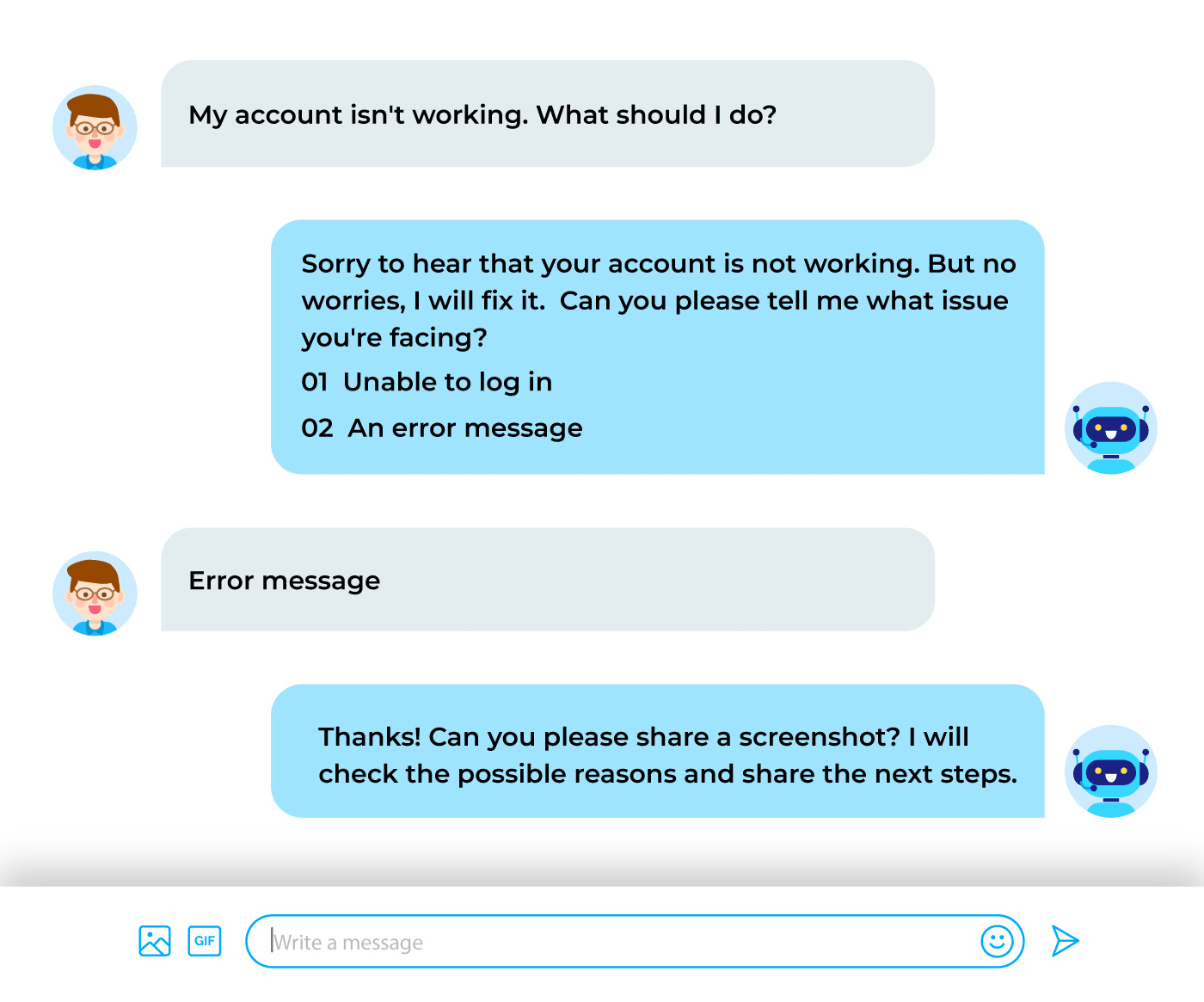
Incomplete Process Automation
RPA isn’t designed to automate complex tasks from end-to-end, but only to automate parts of tasks. Undoubtedly, it’s good when inputs are predictable, but to automate a complete process, it requires interaction with third-party tools such as APIs or varied inputs.
For instance, when a customer raises a support request via email, it may need to be opened, and key details like issue type, priority, and customer ID need to be copied into the ticket system. Well, extracting structure data and entering it into predefined fields is well-suited for RPA; however, the end-to-end process from making to resolving support tickets is not.
How Intelligent Automation Overcomes This
To move past this limitation, Intelligent automation steps in. It doesn’t perform a single repetitive task but manages an end-to-end support process, involving comprehending the issue, classifying it, analyzing sentiment, prioritizing it, delivering accurate resolution, and updating CRMs.
It streamlines the entire support journey from issue detection to resolution, boosting speed, accuracy, and overall customer experience.
For instance, when a customer reports a refund issue, intelligent automation can capture the request, classify the issue, and analyze sentiment. It then verifies account details from the CRM, cross-checks payment history, identifies discrepancies, and issues a resolution or refund automatically while keeping the customer updated in real time.
Enterprise-scale Challenges
One of the limitations of RPA is scalability. It encounters various challenges, such as:
- Integration with third-party tools: RPA can’t easily connect with other essential tools such as Optical Character Recognition (OCR) solutions, password vaults, code repositories, automated testing tools, or chatbots. So when a workflow needs data from multiple sources, it fails, lacking built-in intelligence and integration flexibility.
- Lack of centralized control over attended bots: RPA bots are fragile; even small systems like UI changes can disrupt automation.
- Inflexible licensing and deployment: RPA often has rigid licensing models; because of this, scalability can become expensive and inefficient.
Therefore, RPA’s scalability limitations are not about hardware or servers, but about integration, management, and adaptability.
How Intelligent Automation Overcomes This
Intelligent automation addresses RPA’s scalability challenges effectively by enabling seamless integration with various third-party tools, ensuring a smoother connection with CRMs, ERPs, and other enterprise tools.
Intelligent automation also provides robust centralized controls, allowing organizations to manage, control, and update automation from a single platform. Additionally, it adapts to changes automatically, reducing downtime and maintenance efforts, along with more flexible licensing and deployment methods.
With these capabilities, intelligent automation scales seamlessly with expanding business, manages growing ticket volumes, and delivers faster, more consistent service experiences across channels.
Security and governance shortcomings
The adoption of RPA is often hindered by security and governance concerns, especially for enterprises that are customer-facing and heavily regulated. Many RPA systems lack access control, making it challenging to restrict sensitive information across departments.
In addition to this, the lack of advanced encryption, real-time monitoring, or data loss prevention mechanisms raises concerns about spoofed sessions, unauthorized access, or suspicious data transfers.
Additionally, compliance reporting is often manual and fragmented, making it hard to trace and audit every automated process.
How Intelligent Automation Overcomes This
Intelligent automation addresses these limitations through built-in, enterprise-grade security and governance layers. These governance layers include policy and rules of engagement, technical safeguards, human oversight and accountability, continuous learning, and evolution. It ensures role-based access to sensitive information, PII mask, encrypted automation session, bias and fairness detection, and continuous monitoring activities to flag anomalies or policy violations.
Additionally, it ensures that every automated action is traceable, auditable, and compliant with organizational and regulatory policies. The result is a secure, transparent automation ecosystem where data integrity and accountability are maintained at every level.
By establishing secure, transparent, and compliant automation, organizations can build customer trust, ensure data privacy, and maintain compliance even as automation scales across systems and regions.
From Intelligent to Agentic Automation: The Next Frontier
Intelligent automation has already bridged the gap between rule-based bots and adaptive systems. But the journey doesn’t end there. The next wave, Agentic Automation, takes it a step further. Powered by AI agents, it enables systems to reason, act, and adapt autonomously. These agents can manage workflows end-to-end, respond to changing conditions in real time, learn from feedback, and pursue business goals independently.
As a result, organizations can achieve faster decisions, proactive issue resolution, and scalable enterprise-wide automation.
Leverage Next-Gen Automation with SearchUnify Agentic AI Suite
Support organizations that are looking for automation that can think, learn, adapt, scale and make autonomous decisions effortlessly—leverage SearchUnify Agentic AI Suite.
SearchUnify Agentic AI Suite brings the power of agentic automation, automating the entire support cycle. It connects with multiple knowledge resources via prebuilt connectors and employs agentic AI frameworks. These frameworks facilitate multi-agent collaboration, allowing them to complete complex tasks efficiently.
AI agents within SearchUnify Agentic AI Suite learn and refine their performance over time through built-in audit trails and human-in-the-loop feedback mechanisms. It not only enhances support quality but also enhances customer experience (CX) and builds trust in the brand.
Curious to learn more about SearchUnify Agentic AI Suite and how to embrace Agentic automation with it? Click here!
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are three types of Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
RPA is generally classified into three types: attended, unattended, and hybrid automation. Attended bots work alongside humans, unattended bots operate independently without human intervention, and hybrid automation combines both to streamline end-to-end workflows across different departments and business processes.
2. What is the main purpose of intelligent process automation (IPA)?
The main purpose of intelligent process automation (IPA) is to enhance traditional automation with AI, machine learning, and analytics. It helps systems understand, learn, and adapt to changes, allowing enterprises to automate complex, judgment-based tasks and continuously optimize operations for greater efficiency and scalability.
3. How does robotic process automation differ from intelligent automation?
While RPA automates rule-based, repetitive tasks, IPA extends these capabilities by integrating AI, ML, and NLP to handle unstructured data, make data-driven decisions, and learn from outcomes. In short, RPA performs tasks, whereas IPA thinks, learns, and improves automation over time.
4. What are the four stages of process automation?
The four stages of process automation include identifying repetitive processes, analyzing workflows for optimization, automating tasks using the right technologies, and continuously monitoring and optimizing performance. This structured approach ensures automation not only saves time but also evolves to meet changing business needs.
5. What is agentic automation?
Agentic automation leverages intelligent, AI-driven agents that can reason, decide, and act independently to achieve specific outcomes. By combining machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), and decision-making frameworks, these agents go beyond rule-based automation. They adapt to changing contexts, learn from results, and continuously improve performance.
This enables businesses to automate complex, dynamic workflows with minimal human oversight, making automation smarter, more proactive, and outcome driven.





 Last Updated: November 18, 2025
Last Updated: November 18, 2025


